.png?width=312&height=404&name=Whitepaper%20mockup%20Cooling%20RateI%20(612%20x%20792%20px).png)
Measuring Cooling Time in Welding and Metal Additive Manufacturing
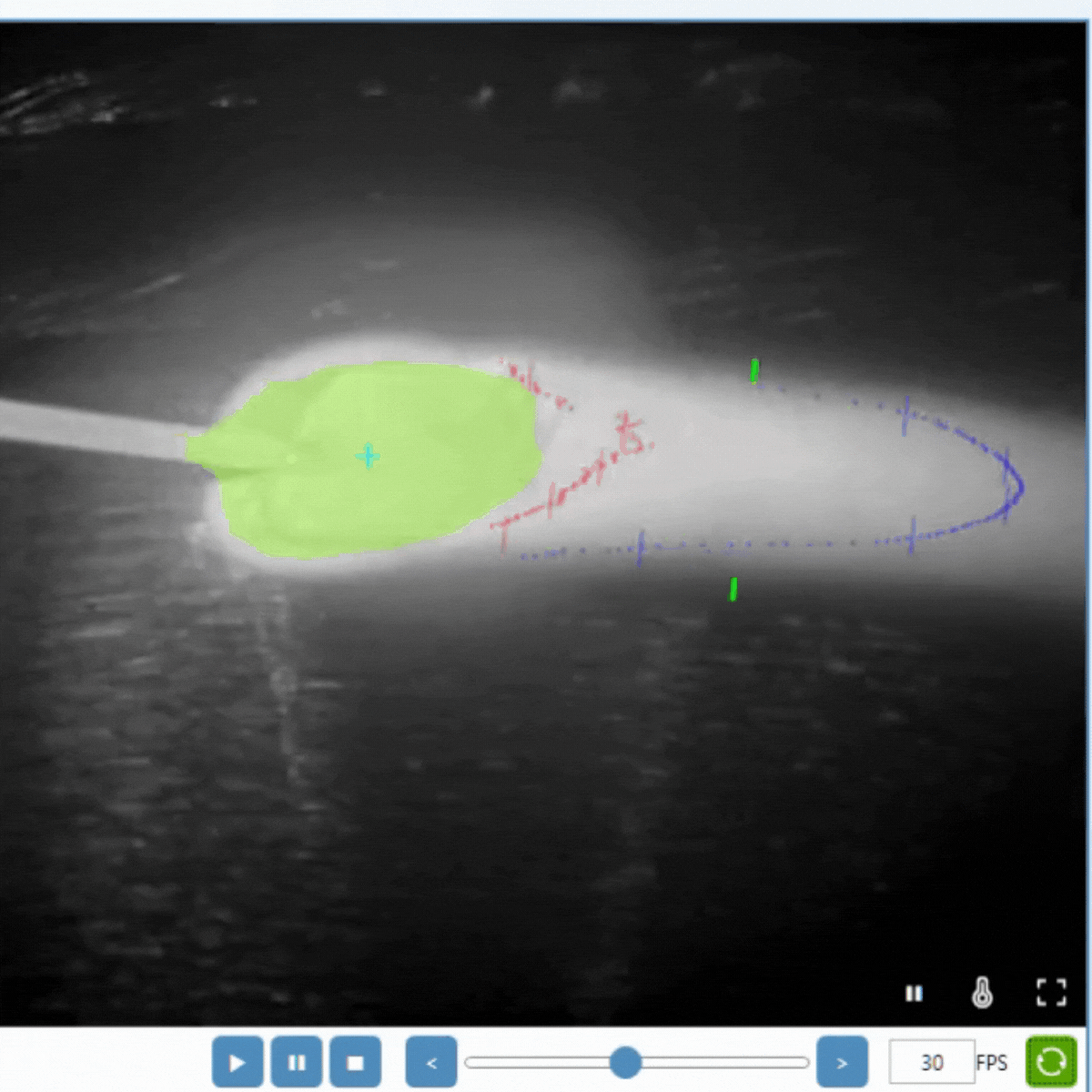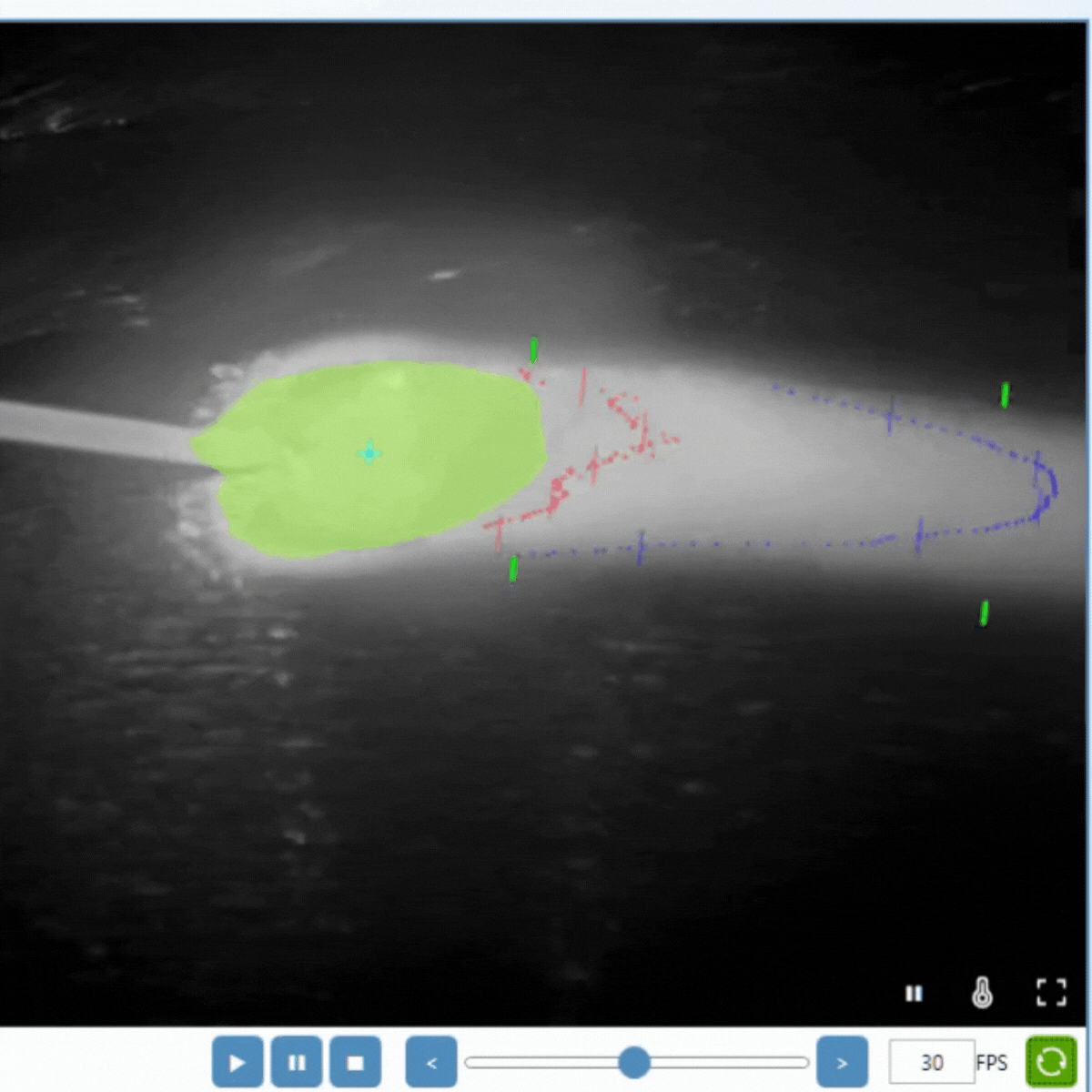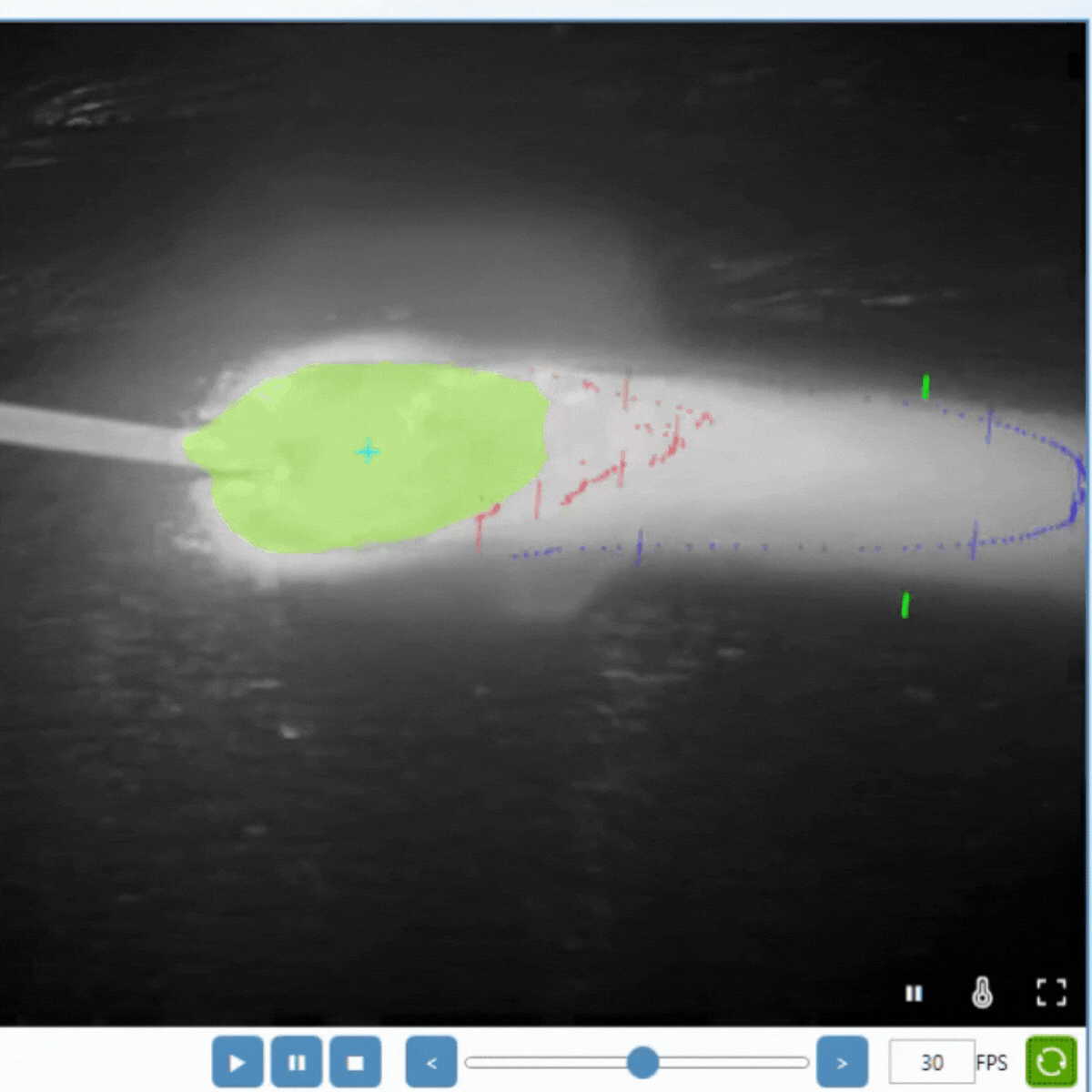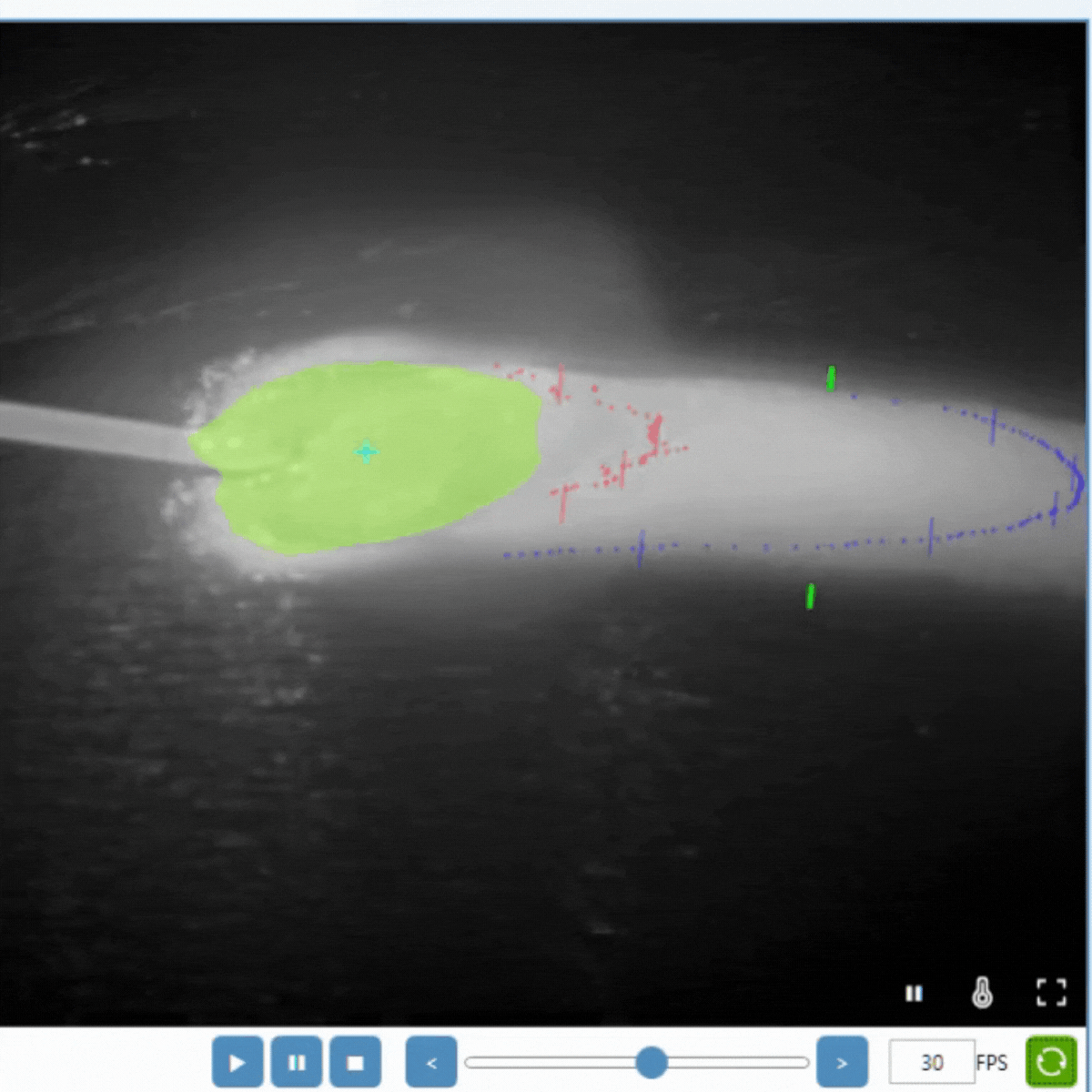
Cooling Time in Welding and Additive Manufacturing (AM)
.gif?width=1200&height=1200&name=Cooling%20Time%20GIF%20-%20Thermal%20Camera%20(2).gif)
.gif?width=1200&height=1200&name=Cooling%20Time%20GIF%20-%20Thermal%20Camera%20(3).gif)
Cooling Time in Metal AM
Metal AM involves building parts layer by layer, and controlling cooling rates is crucial for:
-
Achieving uniform mechanical properties throughout the build.
-
Avoiding defects caused by uneven cooling.
Cooling time measurement applies to both wire-based and powder-based processes, including:
-
Wire-Based Processes: GMAW-based WAAM, Plasma-Arc-based WAAM, Wire Laser AM (WLAM), Wire-based Electron Beam AM.
-
Powder-Based Processes: Laser DED, Laser Powder Bed Fusion, Electron Beam AM.
For wire-based methods like WAAM and WLAM, cooling time measurement is particularly critical. Due to the layer-by-layer nature of these processes, cooling rates can vary significantly within a single build, making accurate monitoring essential.
